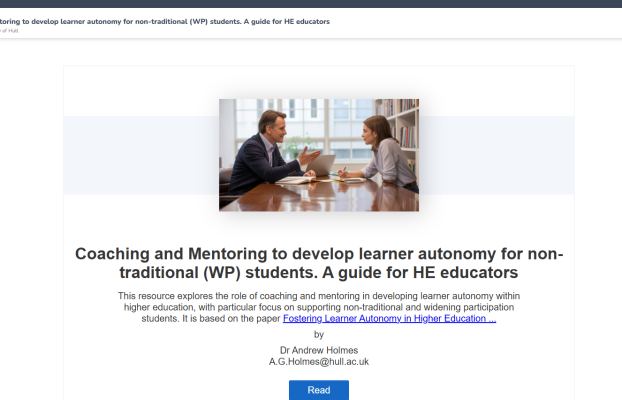
Competence-based Education
The competence-based education framework developed at the University of Hull shifts the focus from what students know to what they can actually do.
The CBE model has three domains: Self Awareness; Disciplinary and Professional Experience; and Knowledge Management, underpinned by our approach to Inclusive Education.
Competence Based Education
Self Awareness
Self-assessment and self-regulation in public and private domains
Disciplinary and Professional Experience
Dialectic action and critical thought to address real-world practice
Knowledge Management
The ability to source, understand and communicate knowledge clearly
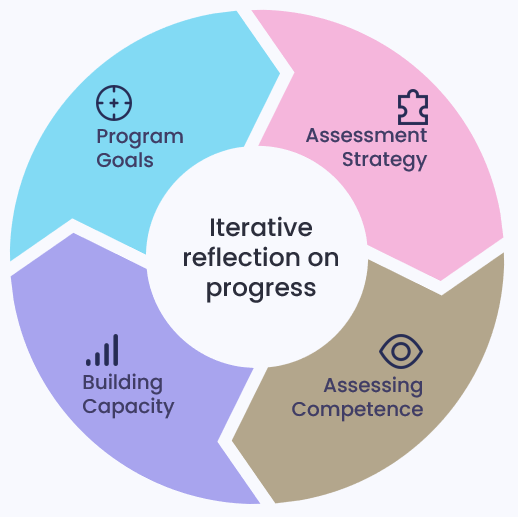
The 5 components of Competency-Based Assessment
Competence-based assessment evaluates individuals based on their ability to demonstrate specific skills and knowledge in real-world tasks, focusing on practical application rather than theoretical knowledge alone.
Relevant
Aligned with the four domains of relevance to student futures: academic, life-long personal, professional, and societal.
Meaningful
Written in jargon-free language that can be understood by all stakeholders and consistently interpreted by them.
Assessable
Some form of activity or output that allows students to evidence their level of competence in a way that is quantifiable.
Valuable
Recognised by key stakeholders as being necessary for the personal and professional future of graduates of the degree.
Meaningful & Engaging
Constructively aligned, requiring students to evidence competencies in contexts that are relevant to their futures
Inclusive, Fair, and Feasible
Seeks to reduce, not reinforce, educational inequalities and awarding gaps for staff and students.
Integrated and Challenging
Developed at the program level before determining disciplinary content, guiding what and when students are taught.
Valuable
Recognised by key stakeholders as being necessary for the personal and professional future of graduates of the degree.
Competence-based
The marking should clearly show how well the submission demonstrates the programme competencies.
Reliable
The grading process is fair, consistent, and transparent, helping students see it as unbiased across levels.
Appropriately Explicit
Criteria should be clear for all stakeholders but flexible enough to allow judgement and encourage creativity.
Developmental
Helps students clearly understand their competence level and supports their growth and self-efficacy.
Institutional literacy
Understanding Higher Education dynamics and navigating institutional rules, expectations, and resources.
Academic literacy
The wide range of skills and attitudes students need to maximise learning gain and attainment.
Attitudinal literacy
Understanding the shift from prior education to Higher Education or between Higher Education study levels.
Educational literacy
The expected skills and knowledge students have when starting the programme or a new study level.
T.B.C
Understanding Higher Education dynamics and navigating institutional rules, expectations, and resources.
T.B.C
The wide range of skills and attitudes students need to maximise learning gain and attainment.
T.B.C
Understanding the shift from prior education to Higher Education or between Higher Education study levels.
T.B.C
The expected skills and knowledge students have when starting the programme or a new study level.
Regular Updates
Competency based education in action. Find out more about education providers results.